What are design organisations according to EASA Part 21J?
At the beginning of each product lifecycle is the design phase, which serves to turn an idea into a marketable product. After market introduction, design activities will once again play a role in case of modifications, refurbishment or major repairs. Design activities in the aerospace industry are unique, since they are subject to exceptional control and surveillance by legislation and aviation authorities. Strict requirements for the design of the product as well as for the company organization and staff qualification should ensure that appropriate attention is paid to safety and reliability during design phase.
Design activities on aeronautical products may only be carried out by EASA approved design organizations. Design organisations in the sense of the EASA are thereby all companies, which develop aeronautical products, parts and appliances, define changes or repair procedures at these. For such activities, organisations must have demonstrated their qualifications to their responsible aviation authority. The requirements for design organisations are defined in the Implementing Rule Initial Airworthiness EASA Part 21 Subpart J (Part 21J for short). Supplementary implementation notes are given by the corresponding AMC and Guidance Material (GM). Regulatory monitoring of design organisations is carried out by EASA or national aviation authorities (NAA).
What are design organizations doing?
The core activities of design organisations include:
- the preparation of design documentation for aeronautical products or changes thereto and the development of repair procedures on such,
- the identification, assignment and interpretation of Certification Specification (CS) and environmental protection regulations,
- the verification that the design is safe and meets the technical airworthiness requirements (Certification Specification – CS),
- the preparation of operating manuals and maintenance manuals,
- the preparation of official design approvals (Type Certification, Supplemental Type Certification or Repair Approvals).
As a result, the design organizations provide Applicable Production Data as well as Applicable Maintenance Data. EASA issues Type Certificate and approvals for repair procedures based on the above activities.
Do you already know our E-Learning for development according to EASA Part 21/J?
- 180 minutes
- Video animated clips with soundtrack
- Certificate is sent automatically after passing the test
- Optionally + Part 21 Safety Management
Requirements for design organizations according to EASA Part 21J
A high level of safety of products must be ensured by a comprehensive quality / design assurance system. The basis for an organisation approval according to EASA Part 21J is the fulfillment of the approval requirements specified in 21A.245:
- The organisation must implement and maintain a quality system in general and a Design Assurance System in particular, to ensure the control and monitoring of all design activities.
- The company must have sufficient personnel in terms of quantity and qualification to carry out the planned design activities.
- Organisational facilities and equipment must enable the employees to carry out their work. In addition to design offices, access to test laboratories and prototyping facilities for showing of compliance must be ensured. In addition to design offices, access to test laboratories and prototyping facilities for showing of compliance must be ensured.
- The organization must enable full and effective collaboration between and within the departments.
- The Organisation must have a handbook that defines and describes its structure, processes and responsibilities.
- All design activities must be covered by the scope of approval. Changes to the scope must be approved by EASA (see 21A.253).
The application process for an organisation approval according to EASA Part 21J
Prior to initial approval as a Part 21J design organisation, EASA checks the fulfillment of the approval requirements in form of an audit. These are repeated at regular intervals to ensure that the organisation can maintain the approval requirements over time. In these surveillance audits, compliance with aviation legisaltion is checked on a random basis. Both before initial approval and during operation, the risk is usually less that individual approval requirements are not met in their entirety, but that they are not fully met. Common deficits in the fulfillment of approval requirements are:
- Procedures are not described clearly,
- the documented procedures are not sufficiently or not completely known to the employees,
- individual employees do not have the required scope of authorization.
Find out now about our services for EASA Part 21J
We support you in training, auditing and safety management according to EASA Part 21J.
Type Certification Process according to EASA Part 21J
Design on aviation products require a complex approval procedure. Before this is not completed, an aircraft may not be allowed to operate, or individual products may not be installed in an aircraft.
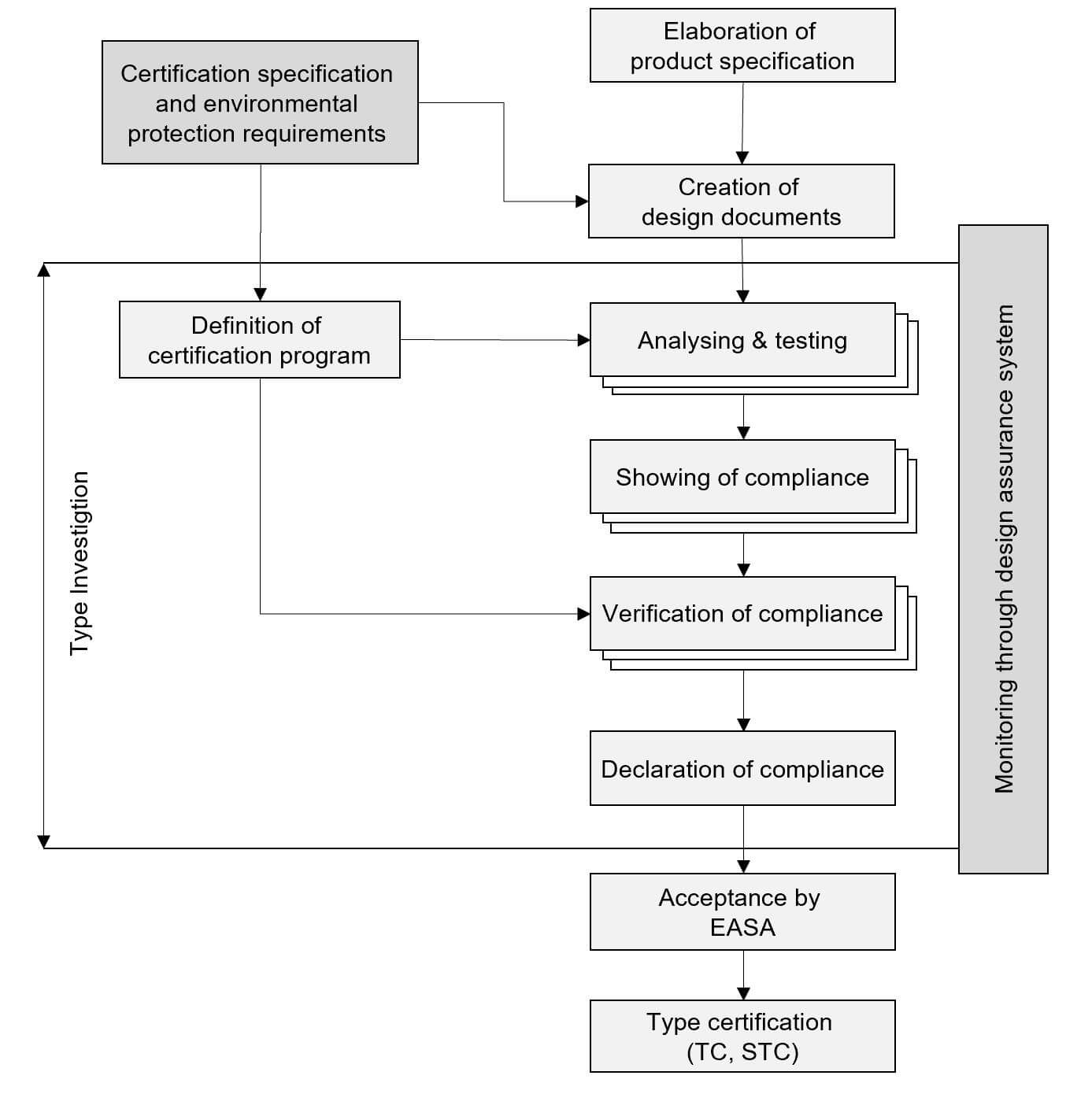
At the beginning of a design process is the preparation of a general description or specification. On this basis, the planned activities should be classified according to their scope and complexity. A distinction is made between the design categories minor and major. Following this classification of the design activity, the certification program (CP) is defined. The CP forms the basis of the typ certification process. In a first step, the applicable Certification Specifications must be identified. The applicability of a Certification Specifications and its showing of compliance (for example by means of tests or calculations) for the individual case is not always clear, so that it needs interpretation.
The following process step, the showing of compliance, is to examine and justify correspondence of the design with the identified Certification Specifications. EASA checks every major design project during the verification of compliance with the Certification Specifications, regardless of whether it is a completely new aircraft or just a modification.
Onc showing of compliance has been finished and the certification program has been successfully completed, the EASA (Agency) issues the type certificate.
Do you need assistance with component approval?
We support you!
Get a non-binding quote at or
+49 (0)40 5131 5291
Certification Specification (CS)
Certification Specifications (CS) Certification Specifications contain detailed requirements for the approval of aeronautical products on a technical level. These CS specify the future design of products while also defining how its airworthiness is demonstrated. While EASA’s Certification Specifications are referred to as Certification Specification (CS), US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) refers to as Federal Aviation Regulations (FAR).
The Certification Specifications of EASA and FAA are similar in structure and also often in its content. In principle, however, divergent terminology used for the interpretation material must be taken into account. EASA refers to this as Acceptable Means of Compliance (AMC), while the JAR refers to Advisory Circular Joint (ACJ) and Advisory Material Joint (AMJ). In the FAA area they are listed as Advisory Circular (AC).
Would you like more information on Certification Specifications?
ETSO products
A special type of approval in design of aeronautical components is the European Technical Standard Order (ETSO). This is a standard for selected parts & appliances used in civil aircraft. This specifies minimum requirements for the performance level or characteristic of the affected products, which are defined in associated Certification Specifications (CS-ETSO). Typical components subject to the ETSO standard are e.g. Instruments, Seats, Tires, Rescue and Safety Equipment and APUs.
The procedure for design, approval and production of ETSO products is regulated in EASA Part 21 Subpart O. Thereafter, an ETSO approval can be applied by any company that demonstrates the necessary design practice and resources for the product. Thus, an EASA Part 21J design organisation approval is not required to apply for an ETSO design.
Prerequisite for a specific product approval by EASA is the submission of comprehensive information regarding design and performance characteristics (DDP – Declaration of Design and Performance).
Would you like to learn more about the approval of ETSO products?
Our Books
Do you already know our books on technical aviation management?


